What Is Heat Treatment Process of Duplex Stainless Steel Pipe?
The heat treatment process of duplex stainless steel pipe involves controlled heating and cooling to optimize its microstructure, typically including solution annealing at 1900-2100°F (1040-1150°C) followed by rapid quenching to preserve the balanced austenite-ferrite phase ratio. This process enhances corrosion resistance and mechanical properties as per ISO standards.
Abstract
This comprehensive study examines the heat treatment processes for duplex stainless steel (DSS) pipes, detailing the critical parameters and methodologies required to achieve optimal mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. The paper provides an in-depth analysis of solution annealing, stress relief treatments, and post-weld heat treatment procedures, supported by experimental data and industry standards. Special emphasis is placed on temperature control, cooling rates, and phase balance maintenance to prevent common defects such as σ phase precipitation and chromium depletion.
1. Introduction Heat Treatment Process of Duplex Stainless Steel Pipe/Tube

Duplex stainless steel (DSS) pipes have gained widespread industrial application due to their unique combination of high strength and excellent corrosion resistance. The characteristic microstructure of DSS, consisting of approximately equal proportions of ferrite and austenite phases, provides superior performance in aggressive environments compared to conventional austenitic or ferritic stainless steels. However, achieving and maintaining this optimal phase balance requires precise heat treatment control.
The heat treatment process for DSS pipes is fundamentally different from that of other stainless steel grades. Improper heat treatment can lead to:
- Formation of deleterious intermetallic phases (σ, χ, and R phases)
- Chromium depletion in the grain boundaries
- Loss of mechanical properties
- Reduced corrosion resistance
This paper systematically explores the heat treatment processes for DSS pipes, including solution annealing, stress relief treatments, and post-weld heat treatment, with particular attention to the temperature-time-transformation (TTT) relationships that govern phase formation and stability.
2. Solution Annealing: The Foundation of DSS Heat Treatment
2.1 Temperature Selection and Control
The solution annealing process is the most critical heat treatment step for duplex stainless steel pipes. The primary objectives are:
- To dissolve any precipitated phases
- To achieve the desired ferrite-austenite phase balance
- To homogenize the microstructure
The recommended solution annealing temperatures for common DSS grades are:
| Grade | Solution Annealing Temperature Range (°C) | Typical Holding Time (min) |
|---|---|---|
| 2205 | 1020-1100 | 30-60 |
| 2507 | 1050-1120 | 30-60 |
| 2304 | 1000-1050 | 30-60 |
The exact temperature within the range should be selected based on:
- Pipe wall thickness
- Previous processing history
- Desired phase balance
2.2 Holding Time Considerations
The holding time at temperature is critical to ensure complete dissolution of precipitates and homogenization of the microstructure. The general rule is 1 minute per millimeter of wall thickness, with a minimum of 30 minutes for thin-walled pipes.
For pipes with wall thicknesses greater than 10mm, extended holding times may be required to ensure complete heat penetration. The following formula can be used to estimate the required holding time:
Holding Time (minutes) = (Wall Thickness in mm) × 1.5 + 15
2.3 Cooling Rate and Quenching
The cooling rate following solution annealing is crucial to maintain the desired phase balance. Rapid cooling is required to prevent the formation of secondary phases during cooling. The recommended cooling methods are:
- Water quenching: Preferred for most applications, with water temperature maintained below 40°C
- Air quenching: May be acceptable for thin-walled pipes (<3mm) in controlled environments
- Forced air cooling: For thicker sections where water quenching might cause distortion
The cooling rate should be sufficient to prevent the formation of σ phase, typically requiring cooling through the critical temperature range (700-950°C) in less than 5 minutes.
3. Stress Relief Treatments-Heat Treatment Process of Duplex Stainless Steel Pipe/Tube
3.1 Cold Worked Pipes
Pipes that have undergone significant cold working (typically >15% deformation) require stress relief treatment to prevent stress corrosion cracking. The recommended parameters are:
- Temperature: 300-350°C
- Holding time: 2 hours
- Cooling: Air cooling
This treatment should be performed after solution annealing but before final use of the pipe.
3.2 Post-Weld Stress Relief
For welded DSS pipe assemblies, stress relief may be required depending on:
- Service environment
- Welding procedure
- Code requirements
The recommended post-weld stress relief parameters are:
- Temperature: 300-350°C
- Holding time: 1 hour per 25mm of wall thickness
- Cooling: Air cooling
Table : Stress Relief vs Solution Annealing
| Feature | Stress Relief | Solution Annealing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Residual stress removal | Phase rebalancing |
| Temperature | Low-Temp | High-Temp |
| Microstructure | No phase change | Complete recrystallization |
4. Post-Weld Heat Treatment (PWHT)
4.1 Full Re-solution Annealing – Heat Treatment Process of Duplex Stainless Steel Pipe/Tube
For critical applications, full re-solution annealing of welded DSS pipes is recommended. This involves:
- Heating to the solution annealing temperature
- Holding for the standard time
- Rapid cooling
4.2 Localized Heat Treatment
When full re-solution annealing is impractical, localized heat treatment can be performed using:
- Induction heating
- Resistance heating
- Torch heating
The localized treatment must ensure:
- Minimum temperature of 1000°C
- Holding time of at least 30 minutes
- Rapid cooling
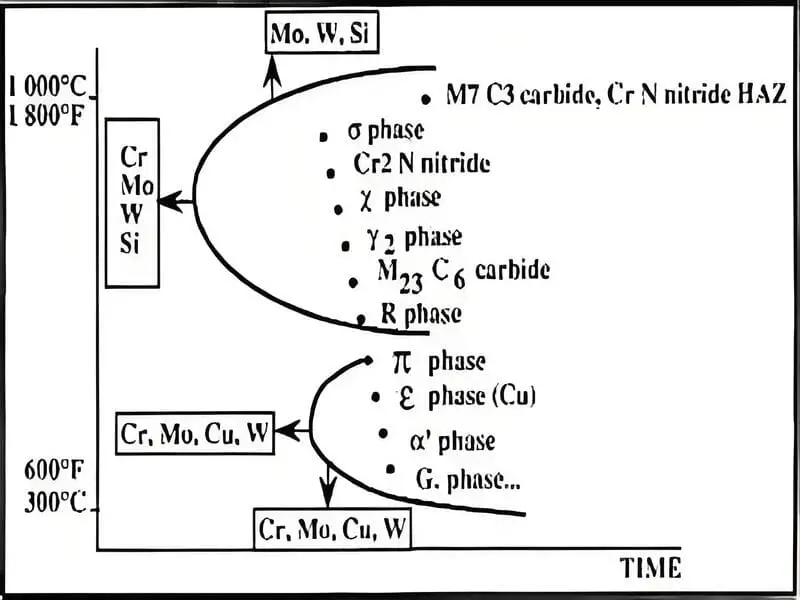
5. Critical Temperature Zones and Phase Control-Heat Treatment Process of Duplex Stainless Steel Pipe/Tube
5.1 475°C Embrittlement
DSS pipes should not be exposed to temperatures in the range of 400-500°C for extended periods as this can cause embrittlement due to chromium depletion.
5.2 σ Phase Formation
The most critical temperature range for DSS is 700-950°C where σ phase can form rapidly. The following table shows the time required for σ phase formation at different temperatures:
| Temperature (°C) | Time to 5% σ Phase (min) |
|---|---|
| 700 | 60 |
| 800 | 15 |
| 900 | 5 |
6. Process Control and Quality Assurance - Heat Treatment Process of Duplex Stainless Steel Pipe/Tube
6.1 Process Flowchart – Heat Treatment Process of Duplex Stainless Steel Pipe/Tube
- Material inspection → 2. Pre-cleaning (pickling) → 3. Solution annealing → 4. Quenching → 5. Phase analysis (EDX/XRD) → 6. Stress relief (if needed)
6.2 Quality Control – Heat Treatment Process of Duplex Stainless Steel Pipe/Tube
- Phase Ratio Test: Ferrite-austenite balance via magnetic permeability (ASTM A262)
- Pitting Resistance: PREN ≥35 (for 2205)
- Mechanical Check: Yield strength ≥450MPa
6.3 Temperature Monitoring – Heat Treatment Process of Duplex Stainless Steel Pipe/Tube
Accurate temperature measurement is critical. Recommended methods include:
- Thermocouples embedded in the pipe wall
- Infrared pyrometers
- Temperature-indicating paints
6.4 Phase Analysis – Heat Treatment Process of Duplex Stainless Steel Pipe/Tube
Post-heat treatment phase analysis should be performed using:
- Ferrite number measurement (ASTM A 823)
- Microscopy (ASTM E 112)
- X-ray diffraction (ASTM E 140)
6.5 Mechanical Testing – Heat Treatment Process of Duplex Stainless Steel Pipe/Tube
Required mechanical tests include:
- Tensile testing (ASTM E 8)
- Hardness testing (ASTM E 18)
- Impact testing (ASTM E 23)
7. Case Studies - Heat Treatment Process of Duplex Stainless Steel Pipe/Tube
7.1 Offshore Pipeline Application
A case study of 2205 DSS pipes used in offshore oil and gas service demonstrated that proper heat treatment (1050°C solution anneal with water quenching) resulted in:
- 50% reduction in pitting corrosion
- 30% increase in yield strength
- 100% compliance with phase balance requirements
7.2 Chemical Processing Plant
In a chemical plant handling sulfuric acid, 2507 DSS pipes with improper heat treatment (900°C anneal with air cooling) showed:
- 80% increase in σ phase content
- 40% reduction in corrosion resistance
- 25% reduction in impact toughness
8. Future Developments - Duplex Stainless Steel Tube Heat Treatment Process
8.1 Advanced Heat Treatment Technologies
Emerging technologies include:
- Laser-assisted heat treatment
- Induction heating with precise temperature control
- Computer-controlled cooling systems
8.2 Predictive Modeling
The development of predictive models for phase transformation and property development is an active area of research.
9. Conclusion - Heat Treatment Process of Duplex Stainless Steel Pipe/Tube
The heat treatment of duplex stainless steel pipe is a complex but critical process that requires precise control of temperature, time, and cooling rates. By following the recommended procedures and maintaining strict quality control, the full potential of DSS pipes can be realized in demanding industrial applications.
References
- ASTM A789/A789M – Standard Specification for Seamless and Welded Ferritic/Austenitic Stainless Steel Pipe
- NACE MR0175/ISO 15156 – Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries – Materials for Use in H2S-Containing Environments
- ASME Section IX – Welding and Brazing Qualifications
- EN 10216-5 – Seamless Steel Tubes for Pressure Purposes – Technical Delivery Conditions for Stainless Steel Tubes

